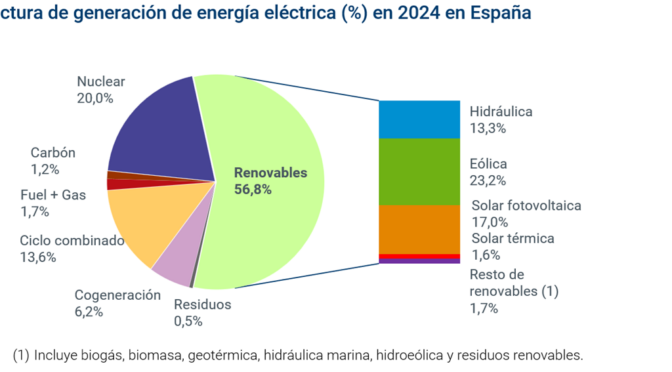
56.8% of all electricity generated in Spain last year used natural sources such as wind energy, photovoltaic, or hydroelectric power.
The Spanish electricity system added 7.3 GW of new photovoltaic and wind power, the largest amount recorded in a single year to date, and a figure that elevates photovoltaic technology to the leading technology in terms of installed capacity. Electricity demand in Spain increased by 1.4% compared to the same period last year, once the effects of working hours and temperatures were adjusted. In 2024, Red Eléctrica commissioned 487 new km of electrical circuits, bringing Spain’s total to 45,674 km. At the time of its creation in 1985, Red Eléctrica had 10,500 km.
Spain closed 2024 with renewable generation of 148,999 GWh (10.3% more than the previous year), representing 56.8% of the total mix. These annual figures, which are the best recorded by Red Eléctrica to date, demonstrate the significant progress of the ecological transition in our country. The boost in installed renewable generation capacity, as well as favorable weather conditions during 2024, allowed hydroelectric power to increase its production by 35.5% compared to 2023 and solar photovoltaic to grow by 18.9%, surpassing its record for the sixth consecutive year.
These are some of the data extracted from the Spanish Electricity System Report 2024 and Renewables in the Spanish Electricity System 2024, two documents by Red Eléctrica, a Redeia company responsible for the transmission and operation of the Spanish electricity system since 1985. These documents analyze the performance of the electricity system during the past year. They were presented today at the Ministry for Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenge at an event that also analyzed the evolution of our energy system over the past few years, on the occasion of the company’s 40th anniversary.
The president of Redeia, Red Eléctrica’s parent company, Beatriz Corredor, highlighted the significant progress experienced by the Spanish electricity system, as “Spain achieved its best indicators in 2024 with a double record in both renewable production and its percentage of the generation mix.” Coinciding with Red Eléctrica’s 40th anniversary, Corredor referred to the transformation of the system over these four decades, “during which we have established ourselves at the forefront of the energy transition in Europe.”
Returning to the 2024 data, wind power leads the national generation structure with 23.2%, followed by nuclear power, with a 20% share, solar photovoltaic (17%), combined cycle (13.6%), and hydropower (13.3%) as the main technologies in our mix.
With this boost from renewables, CO2 equivalent emissions from electricity production reached a historic low in 2024: 27 million tCO2 equivalent, a 16.8% decrease compared to the previous year. Overall, 76.8% of all Spanish energy generated in 2024 was emission-free.
Photovoltaics, the leading technology in an increasingly sustainable generating fleet
During 2024, the Spanish electricity system installed 7.3 GW of new renewable energy, primarily solar photovoltaic and wind technology, representing the largest amount added in a single year.
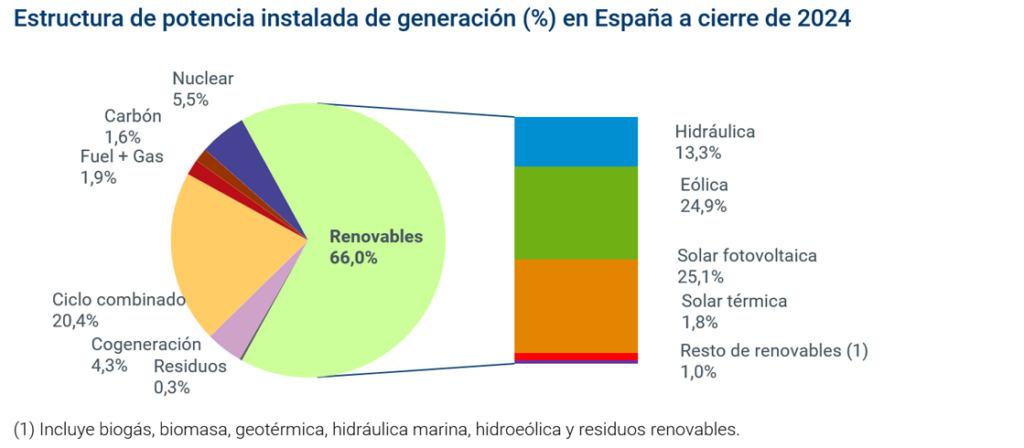
With 6 GW commissioned during 2024, photovoltaics has become the leading technology in the Spanish generating fleet, with a 25.1% share; followed by wind power, which added 1.3 GW this year, reaching 24.9%. In addition to the new production plants that began operations last year, national installed capacity has also been modified by the definitive cessation of operations at the As Pontes coal-fired power plant (in Galicia), which leaves 1.4 GW of non-renewable energy remaining. Thus, by December 31, 2024, Spain will have 129 GW of installed generating capacity, 66% of which is renewable.
“In 1985, the peninsular system only had one renewable technology, hydropower, whereas now we are making better use of all available sources such as wind and solar, and we are integrating 98% of these reliably and safely into the system,” explained Corredor.
New energy storage indicators
Red Eléctrica has included, for the first time, energy storage indicators such as batteries and pumped storage in its annual reports, two technologies that optimize the integration of renewable generation and allow for the subsequent return of energy to the system. For this reason, some of the generation and installed capacity indicators have been updated compared to previous editions, although the company already has the modified data on its various information platforms (Data section of the website, in the redOS app, or in eSios).
In this regard, Spain has an installed storage capacity of 3,356 MW, with which our country has integrated a total of 8,666 GWh this year.
Other figures of the electricity system
In the documents presented today, Red Eléctrica also analyzes other figures such as the evolution of demand, which in 2024 was 1.4% higher than that recorded the previous year, once the effects of working hours and temperatures are taken into account. In gross terms, electricity demand for 2024 was 248,811 GWh, an increase of 0.9%, a variation that remains in line with those of other European countries.
Meanwhile, the transmission grid availability index in the national electricity system reached 98%, while the Balearic and Canary Islands reached 98.5% and 98.8%, respectively.
In 2024, Red Eléctrica added 487 new km of power line circuits, reaching 45,674 km nationwide, a figure far from the 10,500 km that Red Eléctrica had at its inception in 1985.
Over the past 40 years, our country has commissioned several international interconnection projects with neighboring countries such as France and Portugal. This has meant that 2024 will be the third consecutive year that the Spanish electricity system has closed the year as an exporter of electricity to its neighboring countries, with a total of 10,227 GWh.